[ad_1]
It’s estimated that solely round 5% of our oceans have been explored thus far and fewer than 10% mapped utilizing fashionable applied sciences. Leaving 95% unexplored offers extremely huge areas for scientists to work on.
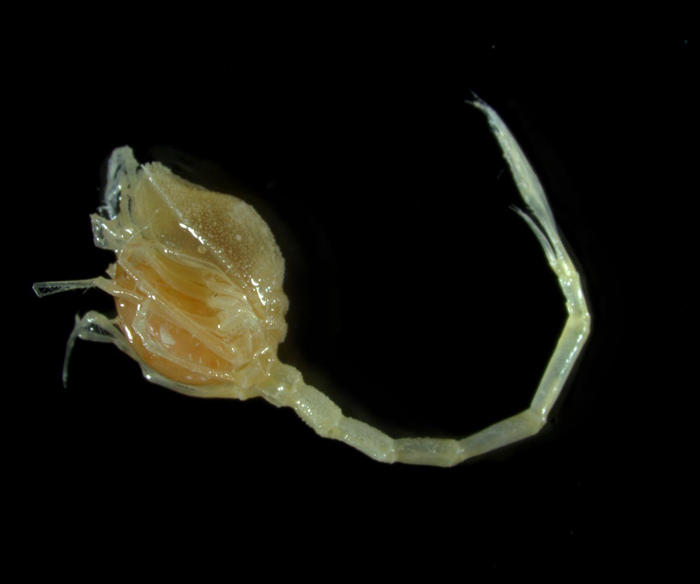
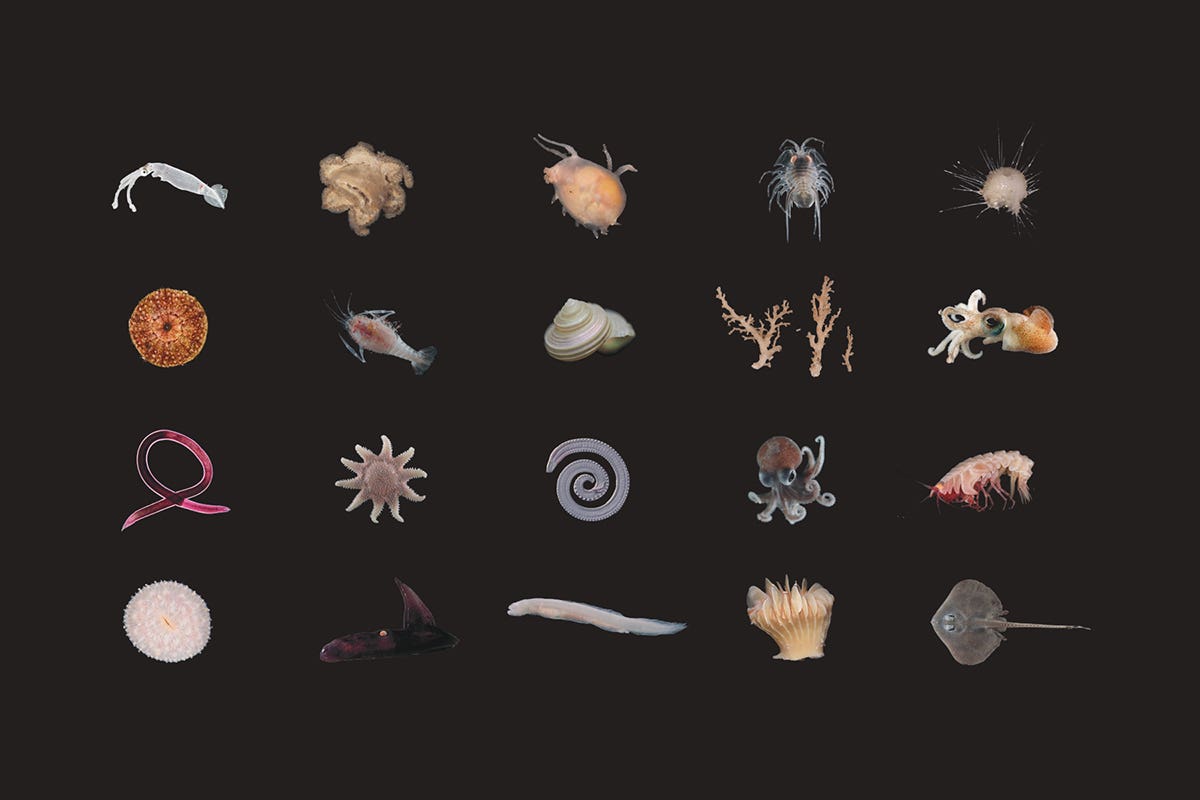
In line with Ocean Census, about 2,200 species are being found every year. Due to this fact, this latest information is really thrilling: a number of weeks in the past, scientists discovered over 100 new marine species within the Bounty Trough, New Zealand, marking a big turning level within the clearer image of the planet’s distinctive biodiversity.
Extra information: Ocean Census
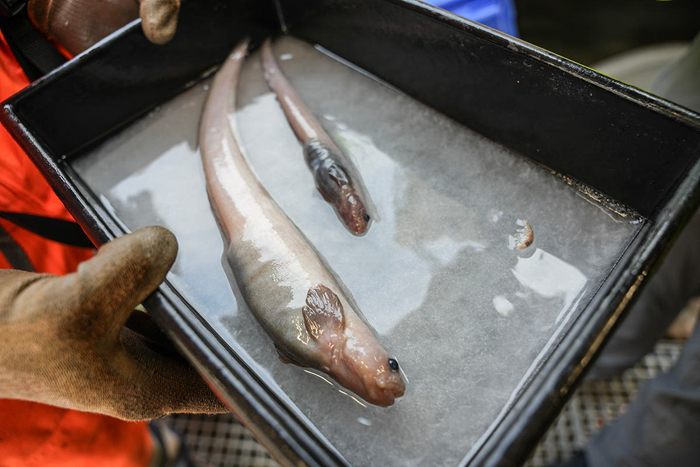
Scientists got here again from the Bounty Trough with thrilling information: over 100 new marine species, together with 3 new species of fish
Picture credit: Ocean Census
Picture credit: Ocean Census
Picture credit: Ocean Census
Picture credit: NIWA Taihoro Nukurangi
Ocean Census is a world alliance of scientists, researchers, philanthropic organizations and a variety of different specialists who’re centered on discovering ocean life from the floor to full ocean depth to have the option to guard the species that stay there.
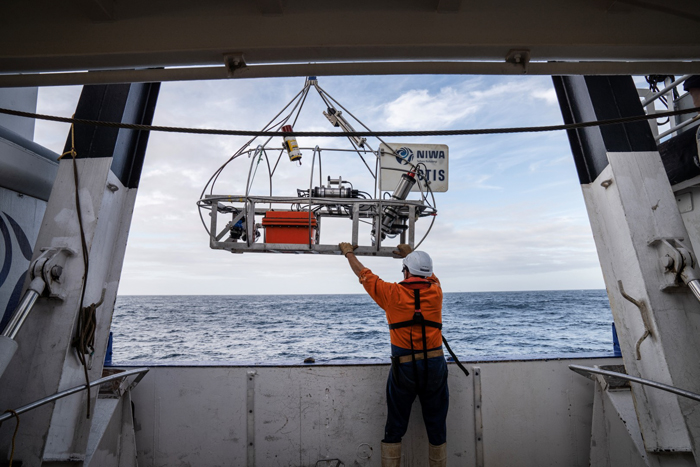
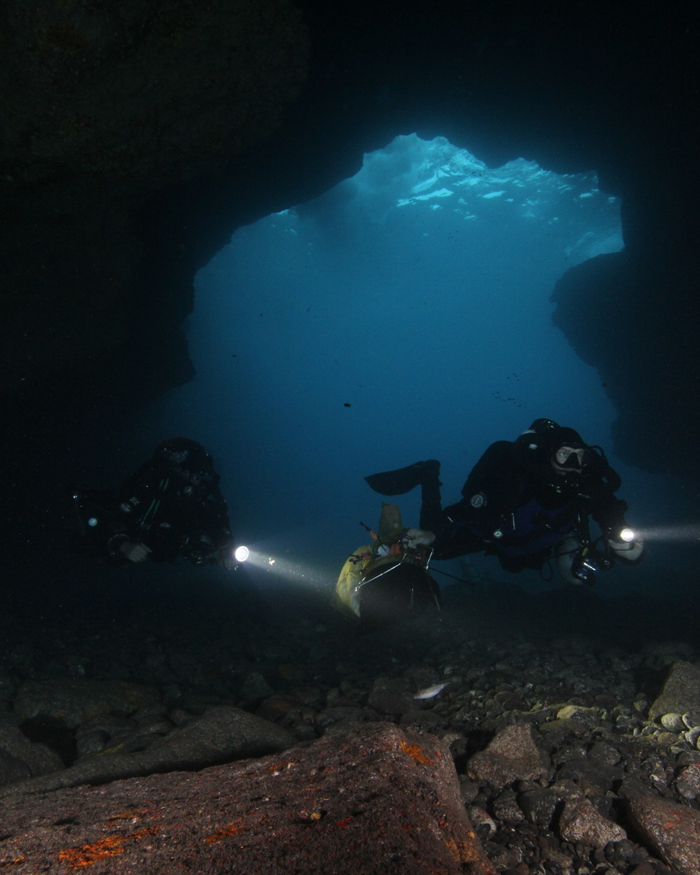
In February, workforce members from Ocean Census, the Nationwide Institute of Water and Atmospheric Analysis in New Zealand (NIWA), and the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa teamed up for a mission to discover the distant Bounty Trough, a deep-water despair situated off the japanese coast of New Zealand’s South Island.
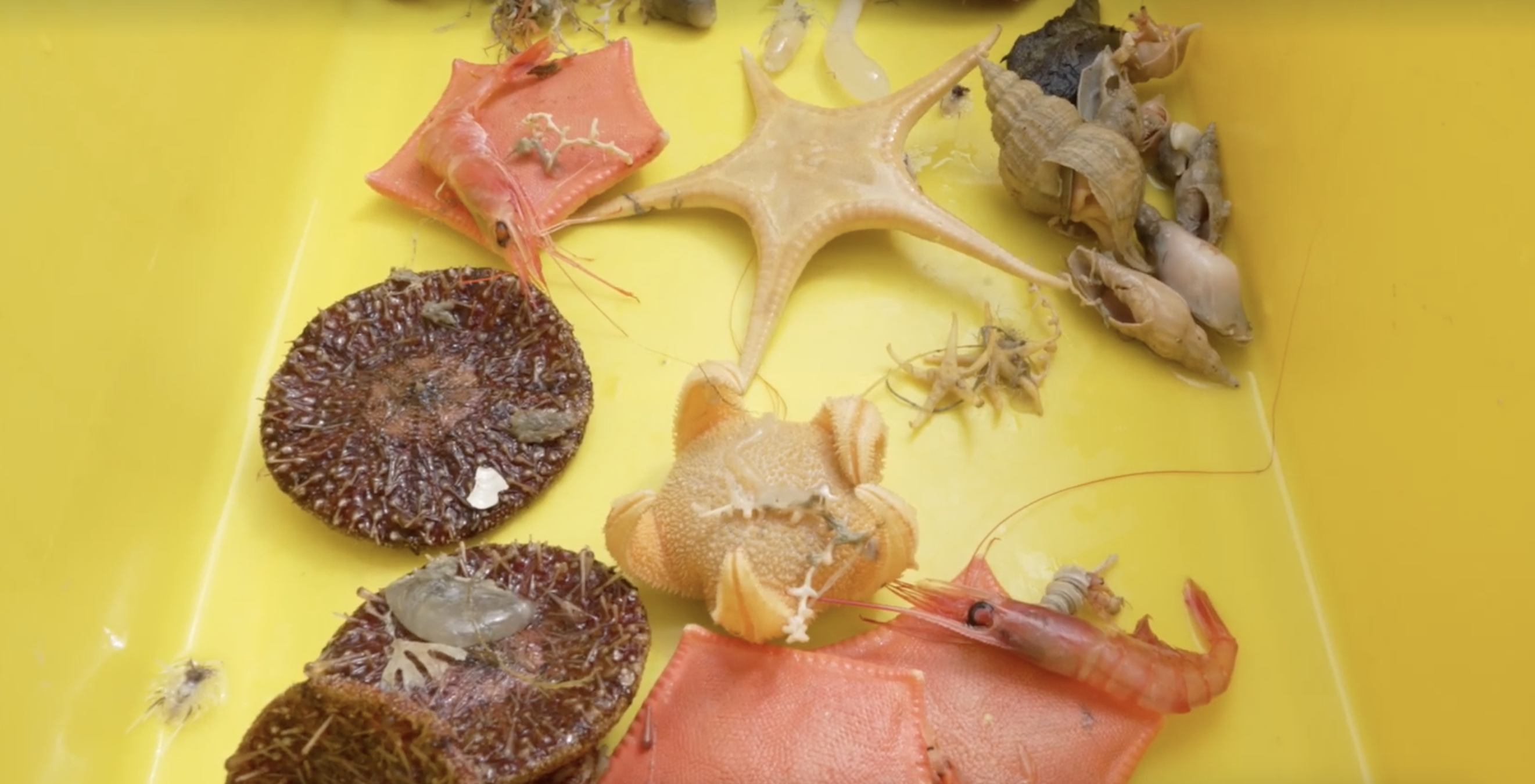
Throughout the three-week expedition, they collected near 1,800 samples, a few of which had been uncovered at depths of greater than 15,000 toes.
The scientists had been impressed with the biodiversity of life they’ve discovered there. “It appears to be like like we’ve an awesome haul of recent, undiscovered species. By the point all our specimens are examined, we might be north of 100 new species. However what’s actually stunned me right here is the actual fact this extends to animals like fish – we predict we’ve received three new species of fish,” stated Ocean Census Science Director Professor Alex Rogers.
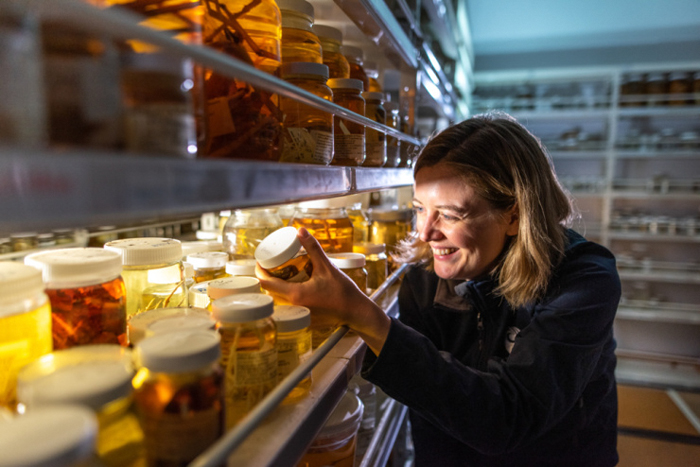
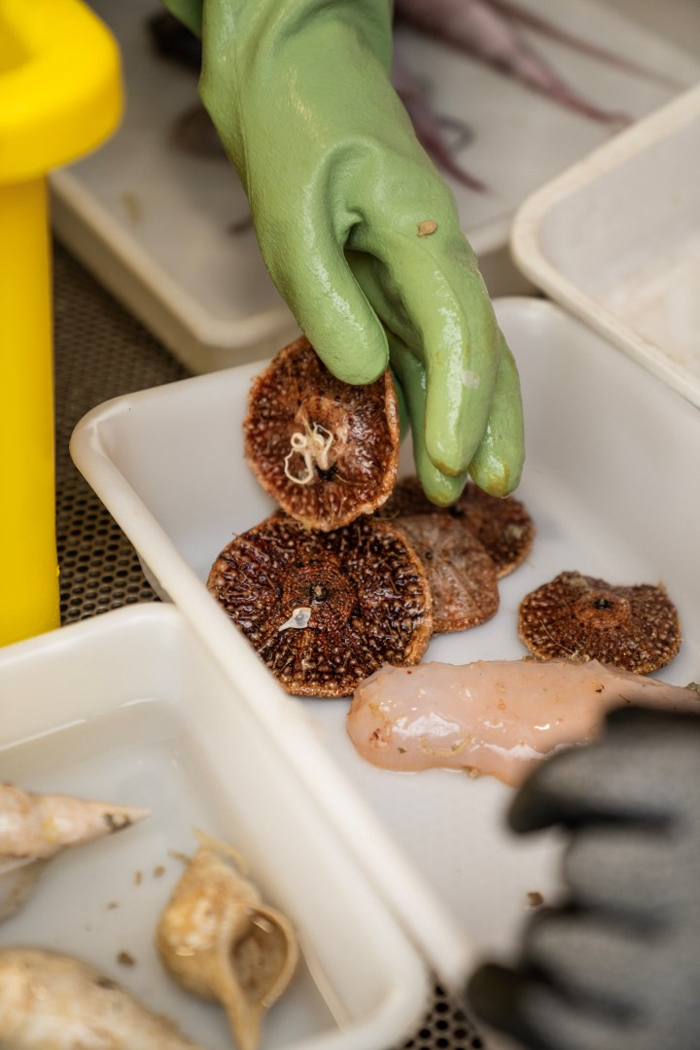
NIWA’s marine biologist Sadie Mills talked about that the expedition has proven the Bounty Trough is flourishing with life: “We’ve gone to plenty of completely different habitats and found a complete vary of recent species, from fish to snails, to corals and sea cucumbers. Actually fascinating species which are going to be new to science.”
Expeditions to under-explored ocean areas just like the Bounty Trough are essential to discovering new species
Picture credit: Ocean Census
Picture credit: Ocean Census
Picture credit: Ocean Census
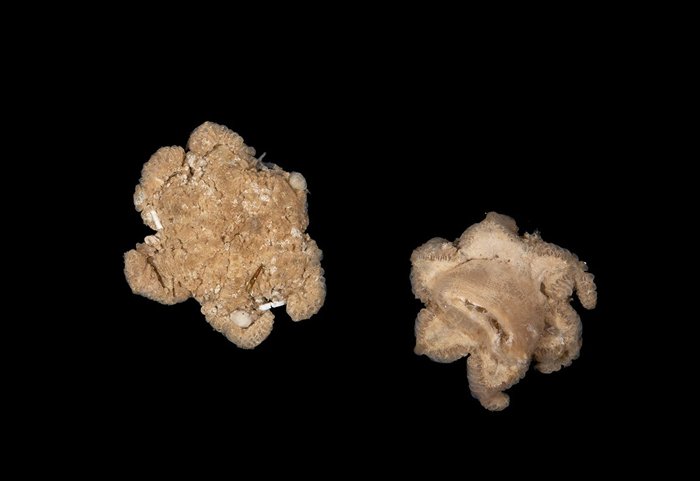
One explicit discover was very exhausting to establish. The specialists first believed it was a brand new sea anemone or a seastar, but taxonomists didn’t wish to agree that it’s both of these species.
Queensland Museum Community taxonomist Michela Mitchell stated that it may very well be a brand new species of octocoral, but additionally a brand new genus. “Much more excitingly, it may very well be a complete new group outdoors of the octocoral. Whether it is, that could be a important discover for the deep sea and offers us a a lot clearer image of the planet’s distinctive biodiversity,” Michela shared the thrill.
Amongst over 100 newly found species may very well be a complete new group outdoors of the octocoral
Picture credit: Ocean Census
Picture credit: NIWA Taihoro Nukurangi
The ocean is fairly deep and huge; subsequently, it’s really difficult by way of scientific discoveries. In line with NOAA and Woods Gap Oceanographic Establishment, the common depth of the ocean is 3,682 meters, or 12,080 toes. It’s additionally recognized that the deepest place within the ocean reaches 10,935 meters (35,876 toes) and is discovered within the Pacific Ocean’s Mariana Trench, at a spot known as Challenger Deep.
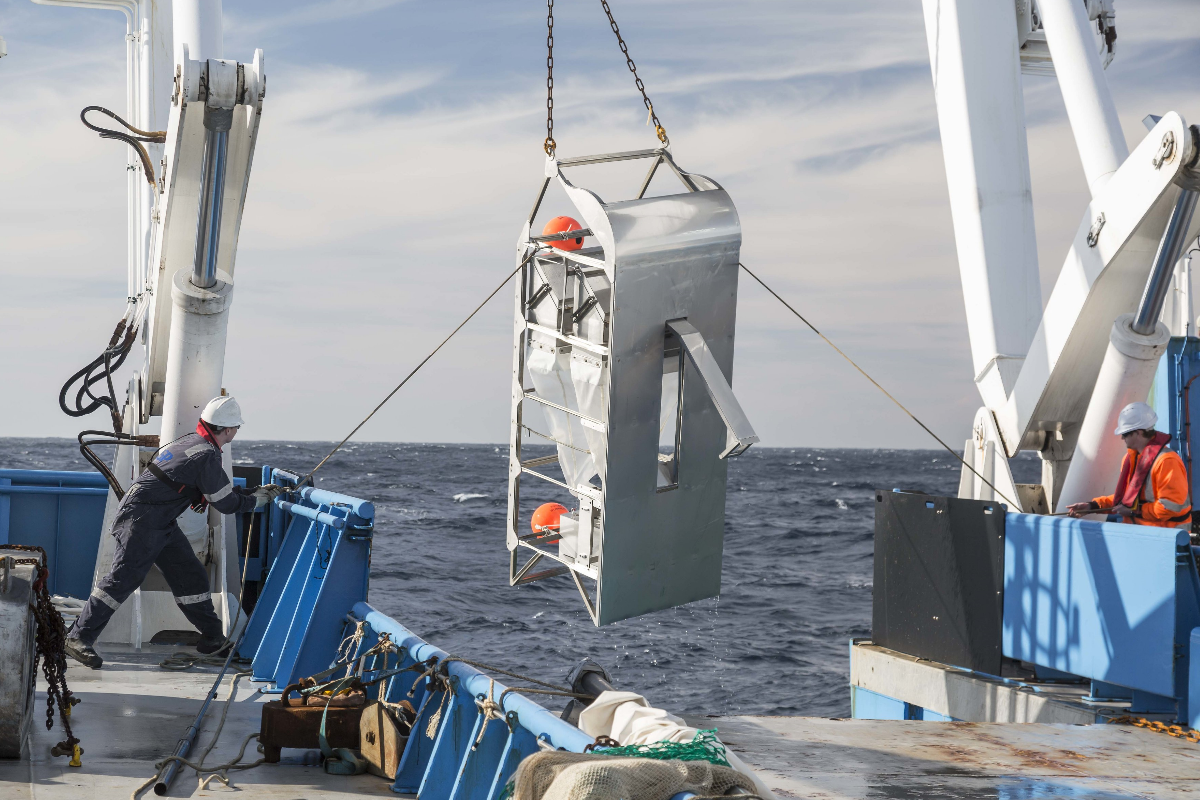
The primary instrument that was used for deep-sea investigation was the sounding weight, utilized by Sir James Clark Ross. Within the 1840s, it reached a depth of about 12,139 toes. These days, for extracting samples from the ocean mattress, scientists usually work with a sampling gadget known as the Brenke sled, which makes use of two nets: one near the seafloor and the opposite one about three toes above that different internet. It drags alongside the ground, catching up the animals that stay shut by.
For these interested by when the primary deep-sea exploration on the planet started, there are not any precise dates, however it goes again to the late 18th or nineteenth century when scientist Pierre-Simon Laplace investigated the common depth of the Atlantic ocean by observing tidal motions registered on Brazilian and African coasts. And the primary deep-sea life kinds had been found in 1864 when Norwegian researchers Michael Sars and Georg Ossian Sars obtained a pattern of a stalked crinoid at a depth of 10,200 toes.
Within the twentieth century, deep-sea exploration superior significantly because of a sequence of technological innovations such because the sonar system, which might detect the presence of objects underwater by way of the usage of sound, manned deep-diving submersibles, and the bathyscaphe Trieste, which in 1960 was despatched into the deepest a part of the world’s oceans by Jacques Piccard and United States Navy Lieutenant Donald Walsh.
Regardless that to many people, sampling susceptible sea creatures could seem to be fairly a radical gesture, it truly offers scientists essential data to be able to improve conservation efforts for threatened and endangered species earlier than it’s too late.
Scientists usually use a Brenke sled – a tool for sampling organisms that stay on and simply above the seafloor
Picture credit: NIWA Taihoro Nukurangi
Picture credit: Marine Biodiversity Hub
Our oceans cowl greater than 70% of the Earth’s floor, but, in accordance with Columbia College’s Earth Institute, scientists know extra about house than the ocean. NASA is on a mission to vary that. By exploring the deep a part of the ocean, they’re looking for clues as to what oceans on different planets may appear like. Surprisingly sufficient, Earth’s depths are similar to among the situations NASA expects to search out on different worlds in our Photo voltaic System.
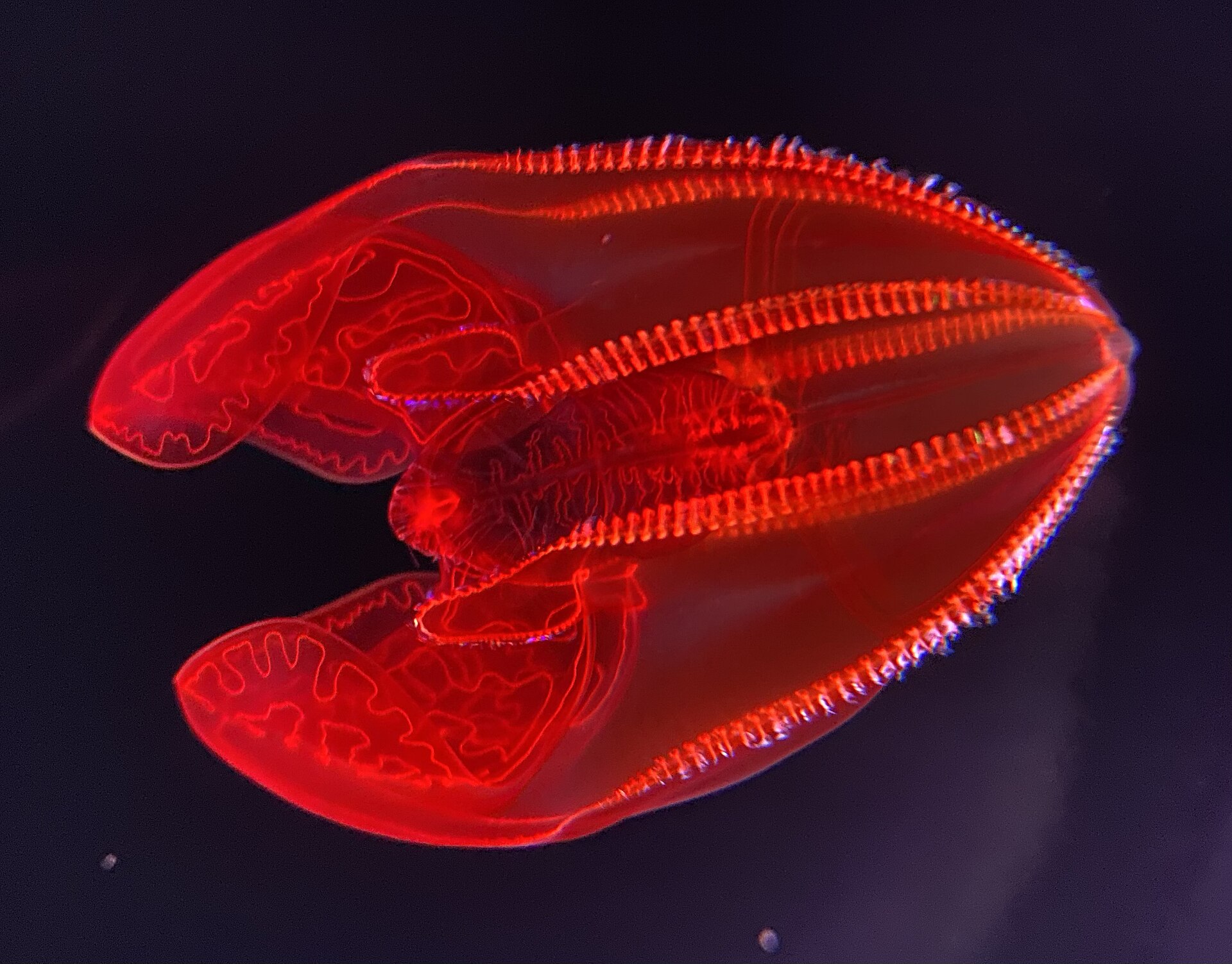
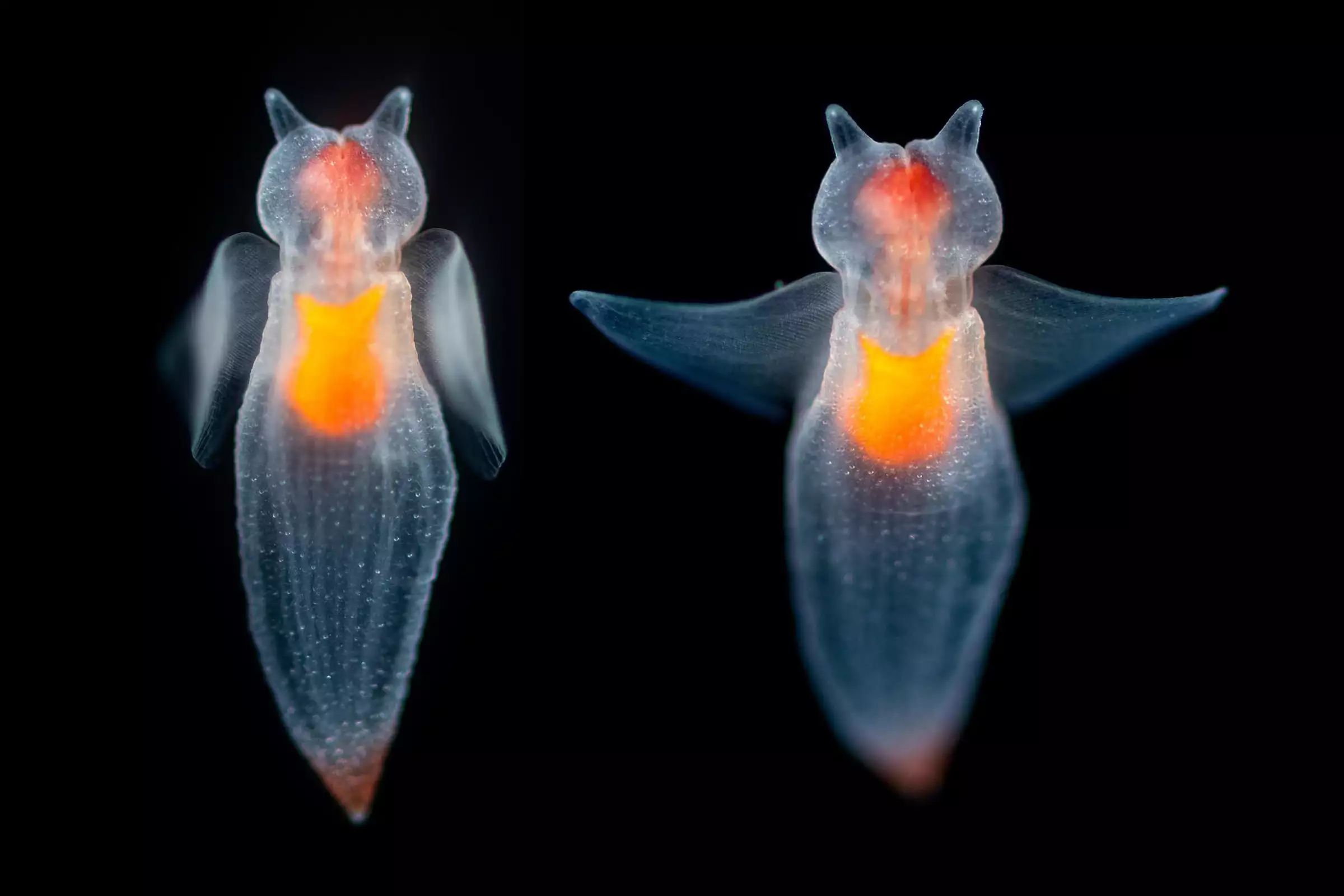
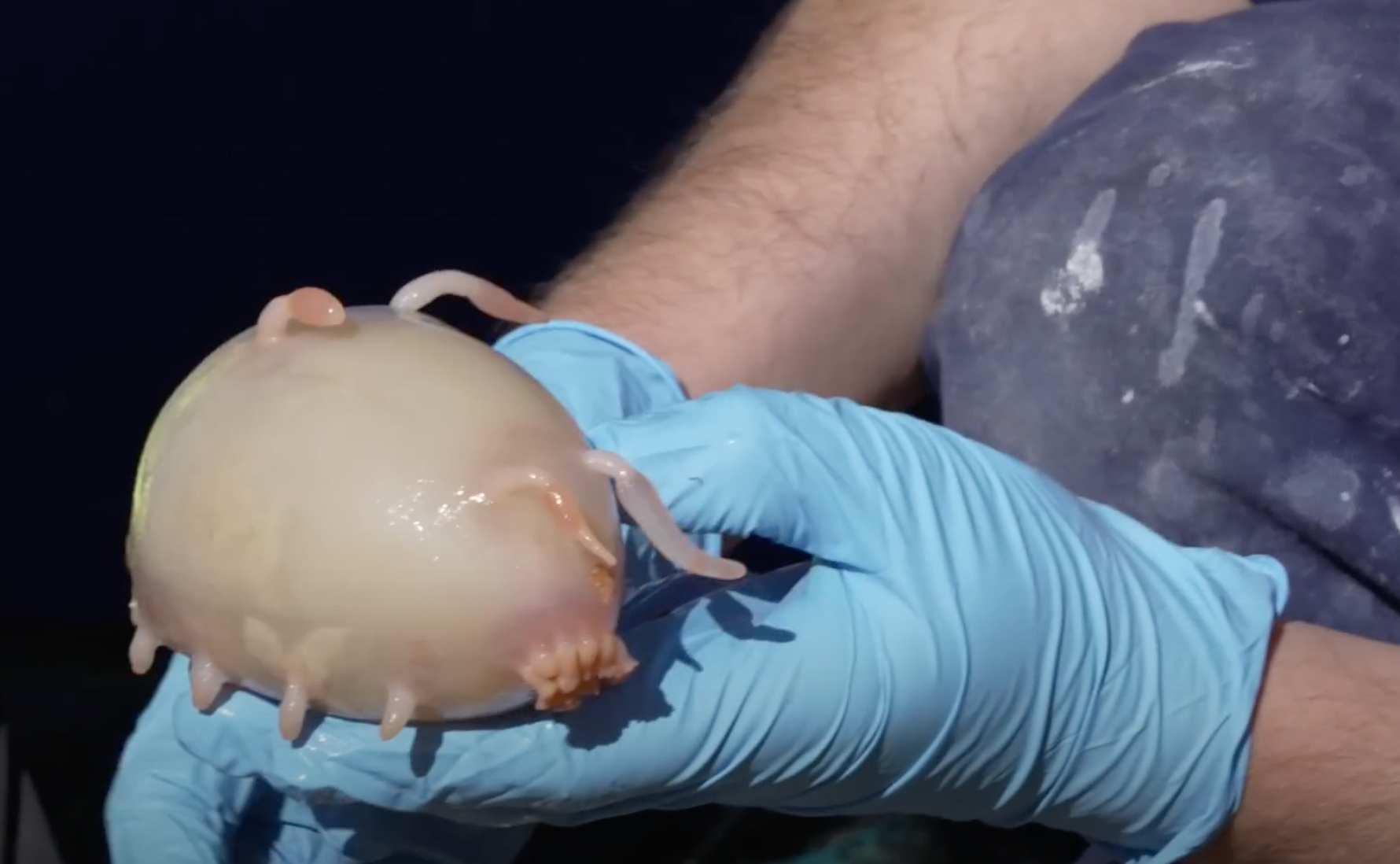
The deepest components of our oceans are known as the hadal zone after Hades, the Greek god of the underworld. This zone happens solely in trenches and mixed all collectively, would make up an space concerning the dimension of Australia. Just a few automobiles can survive plunging into such a darkish abyss and discoveries there may be really fascinating. A few of the all-time weirdest and most fantastic deep sea creatures embrace the bloodybelly comb jelly, sea angel, sea pig, flapjack octopus, anglerfish, stargazer, blowfish, peacock mantis shrimp, pink see-through fantasia, frilled shark, nudibranch, Marrus orthocanna, leafy seadragon, yeti crab and others.
Picture credit: Monterey Bay Aquarium
Picture credit: Monterey Bay Aquarium
Picture credit: Ocean Census
Scientists collected nearly 1,800 samples from the depths of the ocean, discovering species of fish, squid, mollusk and coral which are new to science
Picture credit: Ocean Census
The Ocean Census expedition to the under-explored Bounty Trough is certainly important as a result of the scientists there have amassed a complete lot of information by way of gathering samples, placing the scientific neighborhood in an awesome place to see the place the gaps are. Hopefully quickly we are going to know far more concerning the blue coronary heart of our planet Earth and by elevating consciousness of the significance of marine life, we can get pleasure from these spectacular species for a lot of many years forward.
Folks had been excited concerning the new marine discovery
[ad_2]






 Picture credit:
Picture credit: